The RBI Master Direction aims to enhance the IT governance, risk management, controls, and assurance practices of regulated entities (REs). The Master Direction consolidates and updates previous guidelines on IT governance, risk, controls, assurance practices, and business continuity/disaster recovery management. It applies to scheduled commercial banks (excluding regional rural banks), small finance banks, payments banks, non-banking financial companies, credit information companies, and all India financial institutions. The Master Direction comes into effect from 1 April 2024.
A critical component of the Master Direction is the emphasis on Vulnerability Assessment (VA) and Penetration Testing (PT), collectively known as VAPT. These security assessments are crucial for identifying and mitigating weaknesses in systems that could be exploited by malicious actors.
VAPT Requirements in the RBI Master Direction for IT
The Master Direction outlines specific VAPT requirements for regulated entities, particularly focusing on critical information systems. These are systems that handle sensitive data, have customer-facing interfaces or play a critical role in business operations3. Often, these systems reside in the De-Militarized Zone (DMZ), a network segment that acts as a buffer between the organisation’s internal network and the external internet. Here are the key VAPT requirements:
- Frequency: The Master Direction mandates that critical information systems in the DMZ undergo VA at least once every six months and PT at least once every twelve months. This regular assessment cadence helps entities proactively identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Lifecycle Testing: The Master Direction also requires that VAPT be conducted throughout the entire lifecycle of critical information systems. This includes pre-implementation, post-implementation and after any major changes to the system3. This ensures that security is considered at every stage and that new vulnerabilities introduced during development or modification are identified and mitigated.
- Production Environment Testing: Ideally, PT should be performed in the production environment, which is the live environment where the system is actively used. This provides the most realistic assessment of the system’s security posture5.
- Test Environment Considerations: If testing in the production environment is not feasible, PT can be conducted in a test environment. However, the Master Direction stipulates that the test environment’s version and configuration must closely resemble the production environment to ensure the accuracy of the assessment. Any deviations between the two environments need to be documented and approved by the ISC.
- Remediation: The Master Direction emphasises the importance of timely remediation of vulnerabilities. Regulated entities are expected to take the necessary corrective actions to fix identified vulnerabilities and mitigate associated risks6. This includes addressing known vulnerabilities documented in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database to prevent recurring issues.
- Documentation: Maintaining comprehensive documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance with the Master Direction. Entities must have a documented approach for conducting VAPT that outlines the scope, coverage, vulnerability scoring mechanism (such as the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)) and other relevant details. The Master Direction extends this documentation requirement to information systems hosted in cloud environments as well.
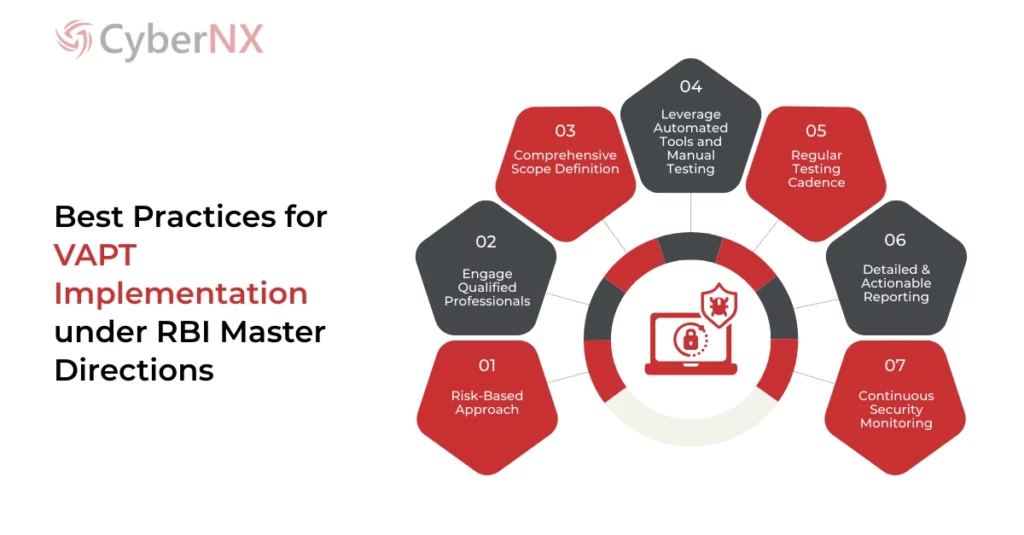
Best Practices for VAPT Implementation
Implementing VAPT effectively requires a strategic approach that aligns with the RBI Master Direction and industry best practices.
- Risk-Based Approach: Not all systems are created equal in terms of their criticality and potential impact. Entities should adopt a risk-based approach to prioritise systems for VAPT assessments5. This means focusing on systems that handle sensitive data, have customer-facing interfaces, or are part of critical business processes.
- Engage Qualified Professionals: VAPT assessments require specialised skills and expertise. Entities should engage qualified security professionals, either internally or through external cybersecurity consulting firms, who have a deep understanding of ethical hacking, vulnerability assessment methodologies and relevant industry standards.
- Comprehensive Scope Definition: The scope of each VAPT engagement should be clearly defined to cover all relevant systems, applications and network components within the defined boundaries. This ensures that no critical assets are overlooked during the assessment.
- Leverage Automated Tools and Manual Testing: Automated vulnerability scanning tools can efficiently identify potential weaknesses. However, it is essential to complement automated scans with manual testing and analysis to verify findings, uncover vulnerabilities automated tools may miss and validate the exploitability of identified weaknesses.
- Regular Testing Cadence: Conducting VAPT assessments regularly is key to maintaining a robust security posture. The testing frequency should be determined based on the RBI Master Direction’s requirements, the organisation’s risk assessment and the evolving threat landscape.
- Detailed and Actionable Reporting: VAPT reports should clearly outline identified vulnerabilities, their severity, potential impact and recommended remediation steps. Reports should be detailed enough to provide IT teams with the information they need to understand and address the findings effectively.
- Continuous Security Monitoring: Implementing continuous security monitoring mechanisms is essential for detecting new vulnerabilities and security threats as they emerge. Organisations should proactively update security policies, procedures and controls to address the ever-changing threat landscape.
VAPT for NBFCs: Why It Matters and What the RBI Expects
Non-Banking Financial Companies depend heavily on digital channels, outsourced platforms, APIs and cloud-first infrastructures. This creates a wider attack surface than many NBFCs realise. Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) helps close these gaps. It also supports the RBI’s broader objective of strengthening cyber resilience across all regulated entities.
The RBI’s Master Directions on IT Governance, Risk, Controls and Assurance Practices positions VAPT as a core assurance activity. For NBFCs, this means VAPT is not just good practice. It forms part of the minimum set of controls expected for secure operations. We often see NBFCs relying on annual audits alone. But the current threat landscape demands frequent testing, deeper validation and validation across third-party integrations.
1. Key Expectations from NBFCs
NBFCs should build a structured VAPT programme that aligns with their risk profile. This starts with identifying critical systems and customer-facing platforms. Most NBFCs run digital journeys across loan origination, onboarding, credit scoring, collections and partner ecosystems. Each step exposes new vulnerabilities. Regular VAPT ensures you are testing every part of this chain.
The RBI also expects VAPT to be carried out by trained and independent security specialists. This is important because NBFCs often work with multiple vendors or rely on in-house teams with limited offensive security experience. Independent testing provides a clearer picture of real-world exposure and reduces blind spots that internal teams may overlook.
2. How VAPT Strengthens NBFC Security
A well-executed VAPT programme helps NBFCs:
- Identify vulnerabilities in core applications, APIs and cloud workloads.
- Detect weaknesses in partner integrations and outsourced environments.
- Validate misconfigurations in backend infrastructure.
- Test authentication, authorisation and session management controls.
- Assess resilience against fraud-driven attacks targeting digital lending journeys.
NBFCs face unique challenges like alternative data ingestion, automated underwriting engines and rapid-scale mobile applications. These systems move quickly. Regular VAPT keeps your security posture aligned with that pace.
3. Why NBFC Boards Should Prioritise VAPT
Boards and senior management of NBFCs are accountable for cyber risk oversight under RBI’s IT governance framework. VAPT reports give them clear, measurable insights into risk exposure. They also help evaluate whether security investments are producing meaningful results. When used well, these insights guide decisions on patching timelines, resource allocation and improvements across IT controls.
How CyberNX Can Help Achieve Compliance with the RBI Master Direction for IT’s VAPT requirements?
CyberNX, a cybersecurity consulting company, can help regulated entities achieve and maintain compliance with the RBI Master Direction’s VAPT requirements. CyberNX can assist with:
- Conducting Comprehensive VAPT Assessments: Using a combination of automated tools and manual techniques, CyberNX’s team of security professionals can conduct thorough VA and PT assessments, ensuring comprehensive coverage and accurate identification of vulnerabilities.
- Providing Actionable Remediation Guidance: CyberNX can provide detailed and actionable recommendations to help entities remediate identified vulnerabilities effectively. Their guidance focuses on minimising risks and achieving compliance in a timely manner.
- Developing a Risk-Based VAPT Strategy: CyberNX works closely with clients to develop a tailored VAPT strategy based on a comprehensive risk assessment. This ensures that the scope and frequency of testing align with the organisation’s specific risk profile and the requirements of the RBI Master Direction.
- Assisting with Documentation and Reporting: CyberNX can help entities generate clear, concise and comprehensive VAPT reports that satisfy the RBI’s documentation requirements. They can also help with developing and maintaining the required documentation for VAPT processes and procedures.
Our RBI Master Directions compliance capabilities go beyond ticking regulatory boxes. We help you turn compliance into a strategic cyber advantage. By aligning controls, strengthening governance, and tightening security operations, we ensure your organisation not only meets RBI expectations but also builds a stronger, more resilient security posture.
VAPT Requirements under RBI Master Directions FAQs
What is the difference between Vulnerability Assessment (VA) and Penetration Testing (PT)?
VA and PT are both crucial security assessments but differ in their approach and objectives. VA is an automated process that scans systems and applications for known vulnerabilities. It relies on a database of known vulnerabilities and compares them to the systems being assessed. PT, on the other hand, involves simulating real-world attacks to identify exploitable weaknesses. It goes beyond simply identifying vulnerabilities by actively trying to exploit them, providing a more realistic assessment of the system’s security posture.
Why is VAPT important in the context of the RBI Master Direction?
VAPT is essential for regulated entities to identify and mitigate security risks, protect sensitive data, ensure business continuity and comply with the RBI’s regulatory requirements. The Master Direction highlights VAPT as a critical component of a robust IT security framework. By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, entities can enhance their security posture, reduce the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches and maintain the trust and confidence of their customers.
Who should be responsible for conducting VAPT assessments?
VAPT assessments should be conducted by qualified security professionals with expertise in ethical hacking and vulnerability assessment methodologies. They should have a thorough understanding of industry best practices, relevant security standards and the specific requirements of the RBI Master Direction. Entities can choose to build internal VAPT capabilities or engage external cybersecurity consulting firms with a proven track record in conducting these assessments.
What steps should be taken after a VAPT assessment is completed?
Once a VAPT assessment is completed, the most important step is to remediate identified vulnerabilities according to their severity and potential impact. The assessment report should provide detailed recommendations for remediation, including specific actions that need to be taken to address each vulnerability. Entities should prioritise remediation efforts based on the criticality of the affected systems and the potential impact of a successful exploit.
How often should VAPT assessments be conducted to comply with the RBI Master Direction?
The RBI Master Direction mandates a minimum frequency for VAPT assessments, particularly for critical information systems. For these systems, VA must be conducted at least every six months, and PT must be conducted at least annually. For other systems that are not deemed critical, a risk-based approach is used to determine the appropriate frequency of VAPT assessments. Factors to consider when determining the frequency include the sensitivity of the data being processed, the system’s exposure to external threats and the organisation’s overall risk appetite.
CyberNX can assist Regulated Entities (REs) in conducting comprehensive gap assessments and achieving compliance with RBI Master Directions. Our services include implementing controls and automating compliance processes, creating dashboards, generating detailed reports, and more. Contact us today to streamline your RBI Master Direction compliance journey.